Clone Object 클래스에는 인스턴스 복사를 위한 clone 메서드가 정의되어 있다.
다음과 같이 Point 클래스가 있다고 하자. Cloneable 인터페이스를 구현하고 있다.
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 public class Point implements Cloneable private int x; private int y; public Point (int x, int y) this .x = x; this .y = y; } public void showPositions () System.out.println(x + " " + y); } @Override public Object clone () throws CloneNotSupportedException return super .clone(); } }
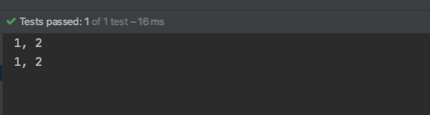
clone 메서드는 다음과 같이 호출해서 사용한다.
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 @Test public void test_clone () Point origin = new Point(1 , 2 ); try { Point copy = (Point) origin.clone(); origin.showPositions(); copy.showPositions(); } catch (CloneNotSupportedException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } }
결과는 다음과 같다.
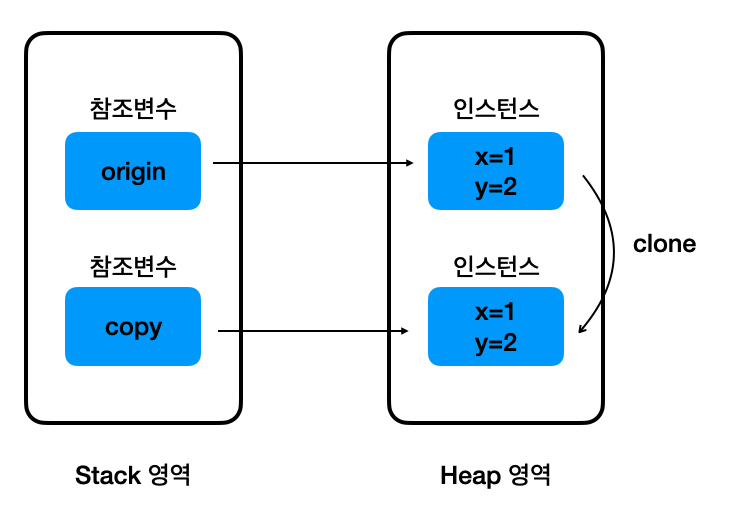
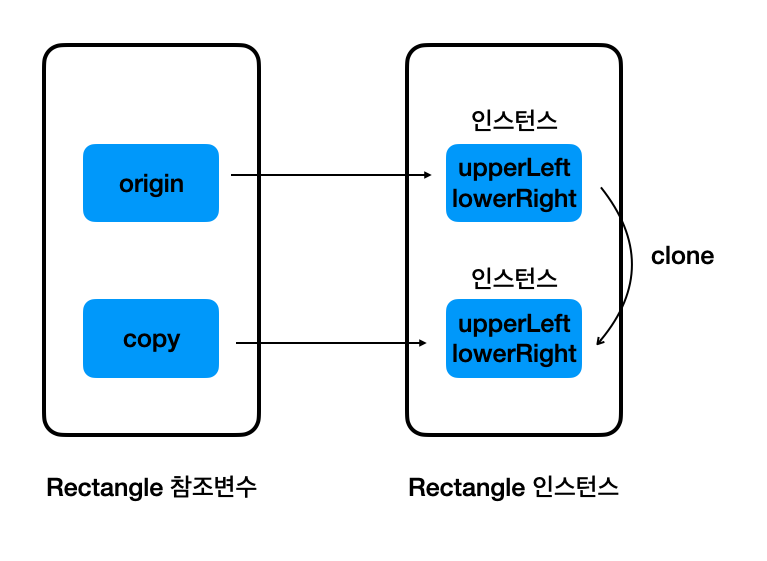
지금까지의 상황을 그림으로 그려 보면 다음과 같다.
Shallow Copy 이번에는 Point 클래스에 changePosition 메서드를 추가해보자.
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 public class Point implements Cloneable private int x; private int y; public Point (int x, int y) this .x = x; this .y = y; } public void showPositions () System.out.println(x + ", " + y); } public void changePosition (int x, int y) this .x = x; this .y = y; } @Override public Object clone () throws CloneNotSupportedException return super .clone(); } }
그리고, 위 Point 클래스를 인스턴스 변수로 가지는 Rectangle 클래스를 추가해보자.
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 public class Rectangle implements Cloneable private Point upperLeft; private Point lowerRight; public Rectangle (int x1, int y1, int x2, int y2) this .upperLeft = new Point(x1, y1); this .lowerRight = new Point(x2, y2); } public void showPosition () System.out.print("upperLeft : " ); upperLeft.showPositions(); System.out.print("lowerRight : " ); lowerRight.showPositions(); System.out.println(); } public void changePosition (int x1, int y1, int x2, int y2) upperLeft.changePosition(x1, y1); lowerRight.changePosition(x2, y2); } @Override protected Object clone () throws CloneNotSupportedException return super .clone(); } }
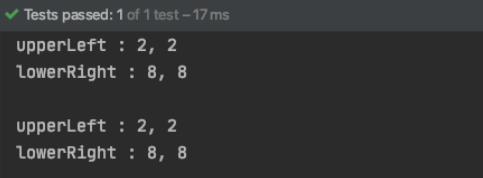
다음과 같이 clone 을 호출하는 clinet code 를 작성해서 실행해보자.
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 @Test public void test_shallow_copy () Rectangle origin = new Rectangle(1 , 1 , 10 , 10 ); Rectangle copy; try { copy = (Rectangle) origin.clone(); origin.changePosition(2 , 2 , 8 , 8 ); origin.showPosition(); copy.showPosition(); } catch (CloneNotSupportedException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } }
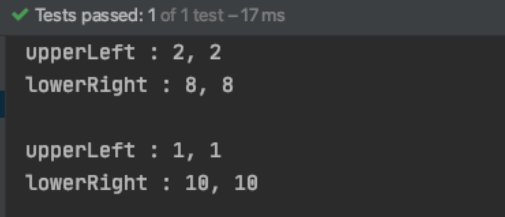
결과는 다음과 같다. origin 의 position 만 변경하였는데도, copy 의 position 까지 변경된것을 알 수 있다.
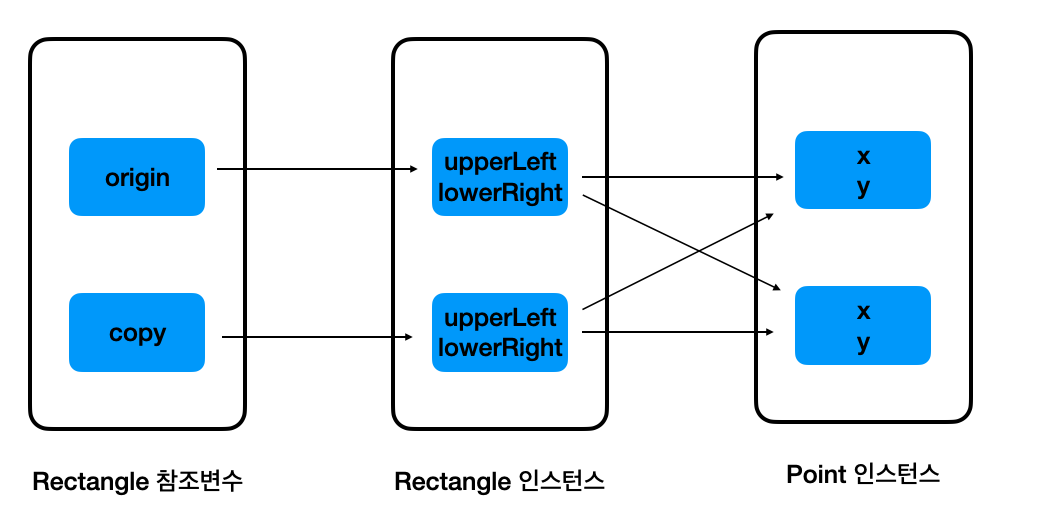
어떻게 이런 결과가 나왔는지 정리해보자. 우선, clone 을 통해서 다음과 같이 Rectangle instance 를 복사하였다.
하지만, Object 클래스의 clone 메서드는 인스턴스의 변수에 저장되어 있는 값을 복사할 뿐, 참조하는 대상 자체를 복사하지는 않는다.
이것이 얕은 복사, Shallow Copy 이다.
Deep Copy 그렇다면, 참조변수가 가리키는 인스턴스 자체를 복사하기 위해서는 어떻게 해야할까 ?
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 public class Point implements Cloneable private int x; private int y; public Point (int x, int y) this .x = x; this .y = y; } public void showPositions () System.out.println(x + ", " + y); } public void changePosition (int x, int y) this .x = x; this .y = y; } @Override public Object clone () throws CloneNotSupportedException return super .clone(); } }
Rectangle 클래스의 clone 메서드를 수정해보자.
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 public class Rectangle implements Cloneable private Point upperLeft; private Point lowerRight; public Rectangle (int x1, int y1, int x2, int y2) this .upperLeft = new Point(x1, y1); this .lowerRight = new Point(x2, y2); } public void showPosition () System.out.print("upperLeft : " ); upperLeft.showPositions(); System.out.print("lowerRight : " ); lowerRight.showPositions(); System.out.println(); } public void changePosition (int x1, int y1, int x2, int y2) upperLeft.changePosition(x1, y1); lowerRight.changePosition(x2, y2); } @Override protected Object clone () throws CloneNotSupportedException Rectangle copy = (Rectangle) super .clone(); copy.upperLeft = (Point) upperLeft.clone(); copy.lowerRight = (Point) lowerRight.clone(); return copy; } }
그리고 이제 client code 에서 실행해보자.
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 @Test public void test_deep_copy () Rectangle origin = new Rectangle(1 , 1 , 10 , 10 ); Rectangle copy; try { copy = (Rectangle) origin.clone(); origin.changePosition(2 , 2 , 8 , 8 ); origin.showPosition(); copy.showPosition(); } catch (CloneNotSupportedException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } }
결과는 다음과 같다. shallow copy 와 다르게, origin 의 position 을 변경하였지만, copy 에는 영향이 없다.
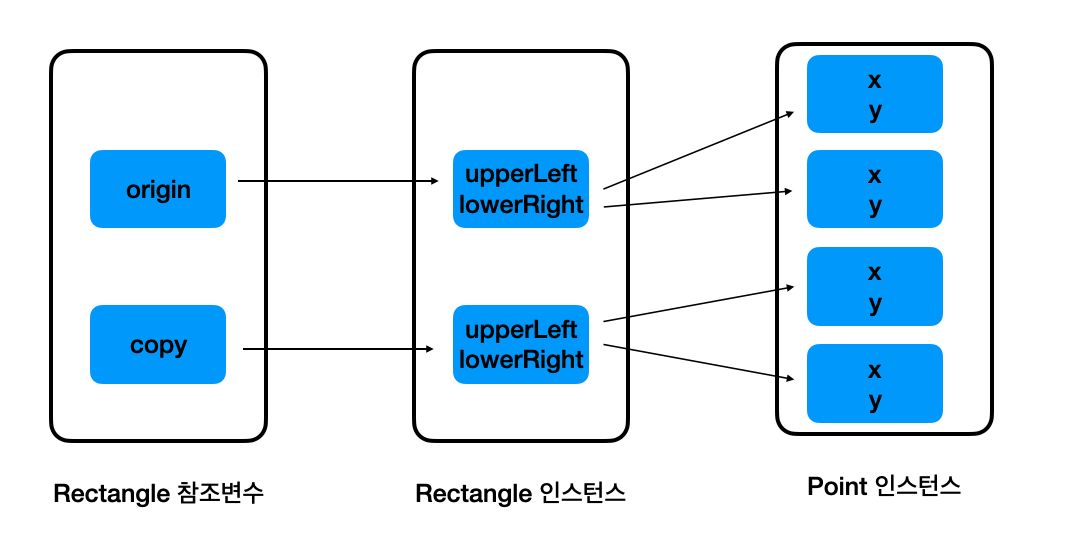
지금까지의 상황을 정리하면 다음과 같다.
이것이 깊은 복사, Deep Copy 이다.
String Copy 인스턴스 변수가 String 인 경우를 고려해보자. 우선 다음 코드를 보자.
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 public class Person implements Cloneable private String name; private int age; public Person (String name, int age) this .name = name; this .age = age; } public void changeName (String name) this .name = name; } public void showPerson () System.out.println("name : " + name); System.out.println("age : " + age); System.out.println(); } @Override protected Object clone () throws CloneNotSupportedException return super .clone(); } }
그리고, 위 Person 을 복사하는 다음 코드가 있다.
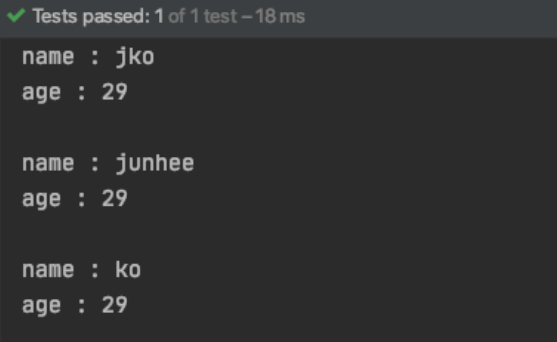
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 @Test public void test_string_copy () Person jko = new Person("jko" , 29 ); try { Person junhee = (Person) jko.clone(); junhee.changeName("junhee" ); Person ko = (Person) junhee.clone(); ko.changeName("ko" ); jko.showPerson(); junhee.showPerson(); ko.showPerson(); } catch (CloneNotSupportedException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } }
실행 결과는, deep copy 와 같이 서로 영향이 없다.
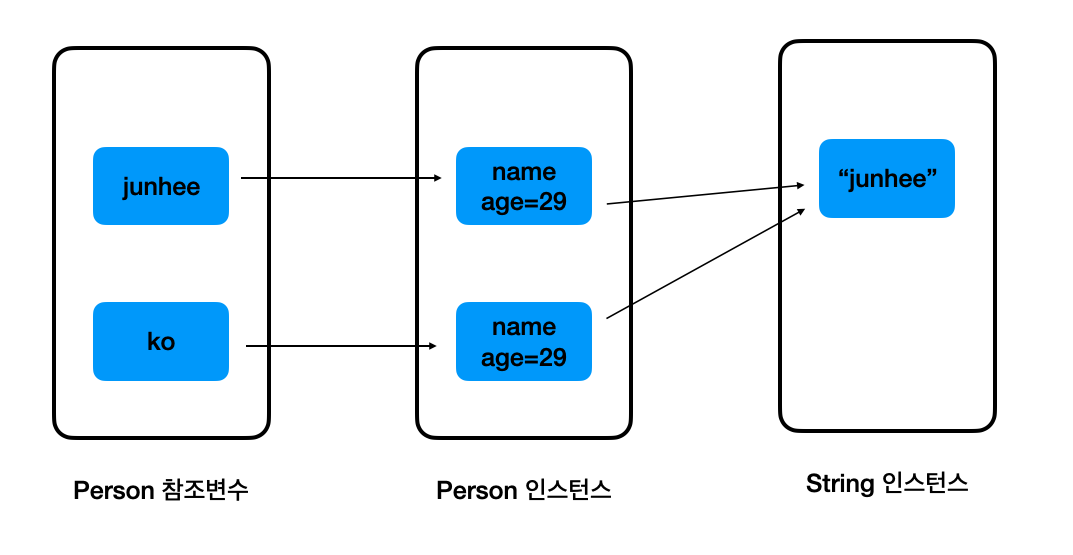
어떻게 이렇게 되었는지 확인해보자. 우선, 처음에 junhee 를 clone 하였을 때 상황은 다음과 같다.
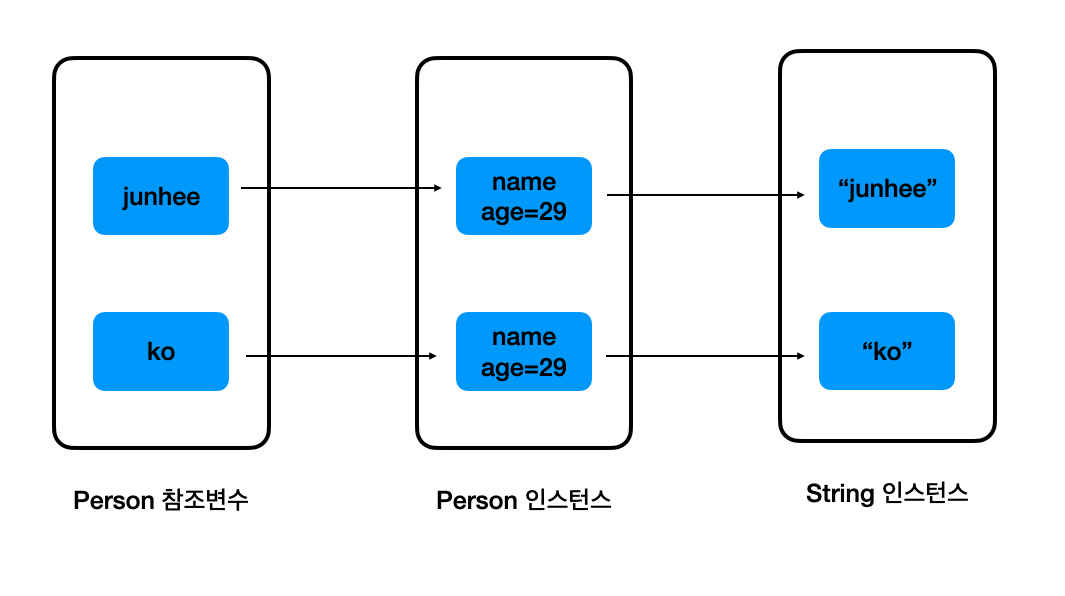
그리고, ko 가 참조하는 인스턴스의 문자열을 변경시킨다. 그러면 결과는 다음과 같다.
난 정말 JAVA 를 공부한적이 없다구요 <윤성우>