Collection Framework - Iterable
Collection 인터페이스는 아래과 같이 Iterable 인터페이스를 상속하고 있다.
Iterable 인터페이스가 무엇인지 정리해보자.
1. Iterator
Iterable 인터페이스에는 다음 세개의 메서드가 정의되어 있다.
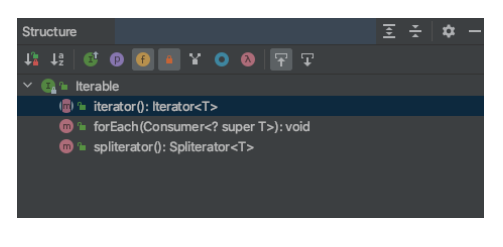
여기서 iterator 메서드가 정의되어 있는데, Iterator 인터페이스를 반환한다.
즉, iterator 메서드를 호출하면 Iterator 인터페이스를 구현한 클래스의 인스턴스 참조 값을 반환한다.
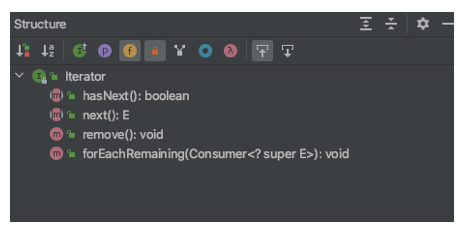
그리고 Iterator 인터페이스에는 다음 네 개의 메서드가 정의되어 있다.
Iterator 의 사용법은 아래와 같다.
1 | public class IteratorExample { |
LinkedList 의 iterator() 를 호출하면,
LinkedList 가 상속하고 있는 추상 클래스인 AbstractSequentialList 의 iterator() 가 호출이 된다.
2. 필요성
그런데, Collection 인터페이스가 Iterable 인터페이스를 상속하고 있는 이유가 뭘까 ?컬렉션 클래스의 종류에 상관없이 일관된 형태의 데이터 참조방식을 지원하기 위해서이다.
예를들면,
List 인터페이스를 구현하고 있는 LinkedList 나, Set 인터페이스를 구현하는 HashSet 이나 모두 동일한 방식으로 데이터 참조가 가능하다.
난 정말 JAVA 를 공부한적이 없다구요 <윤성우>